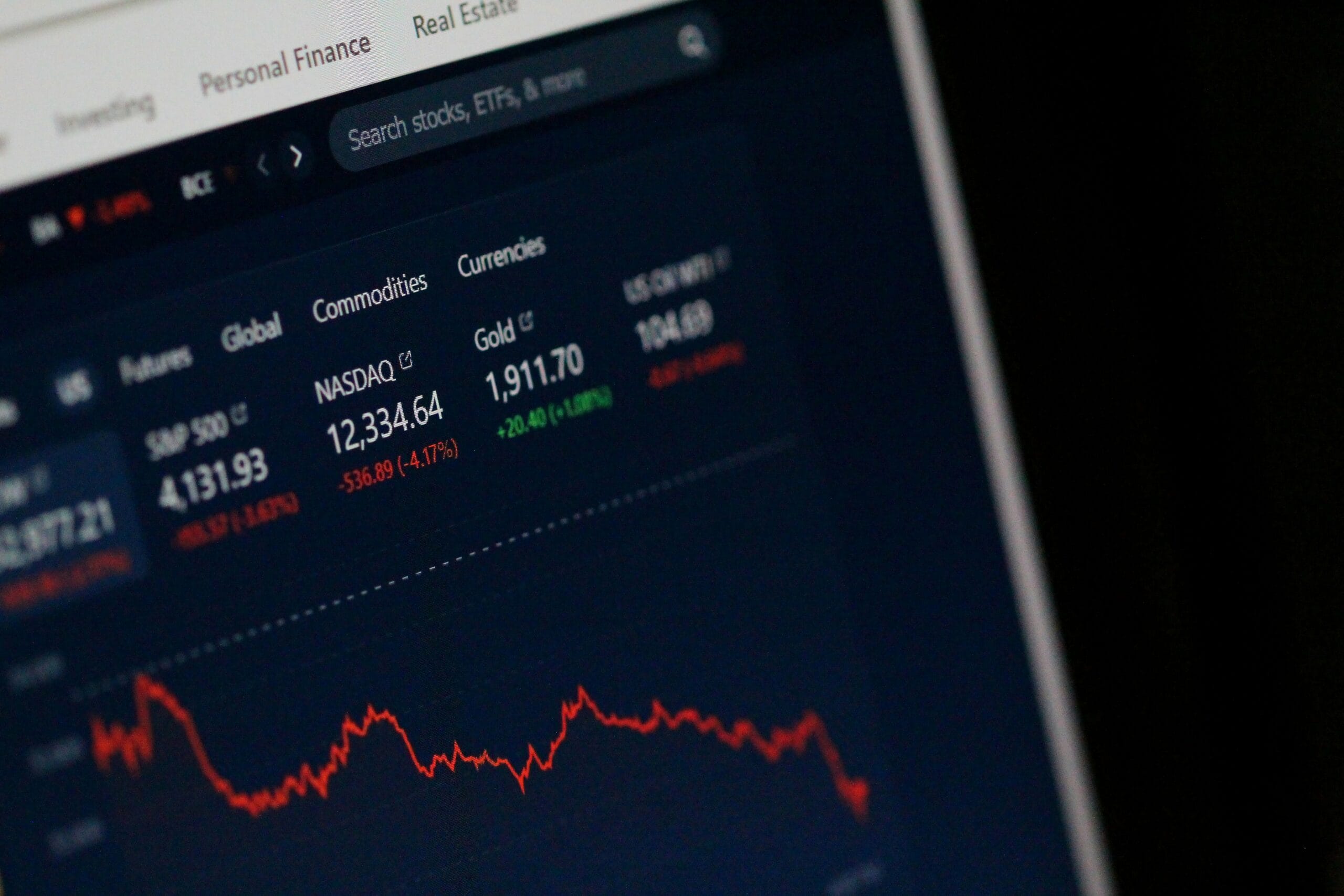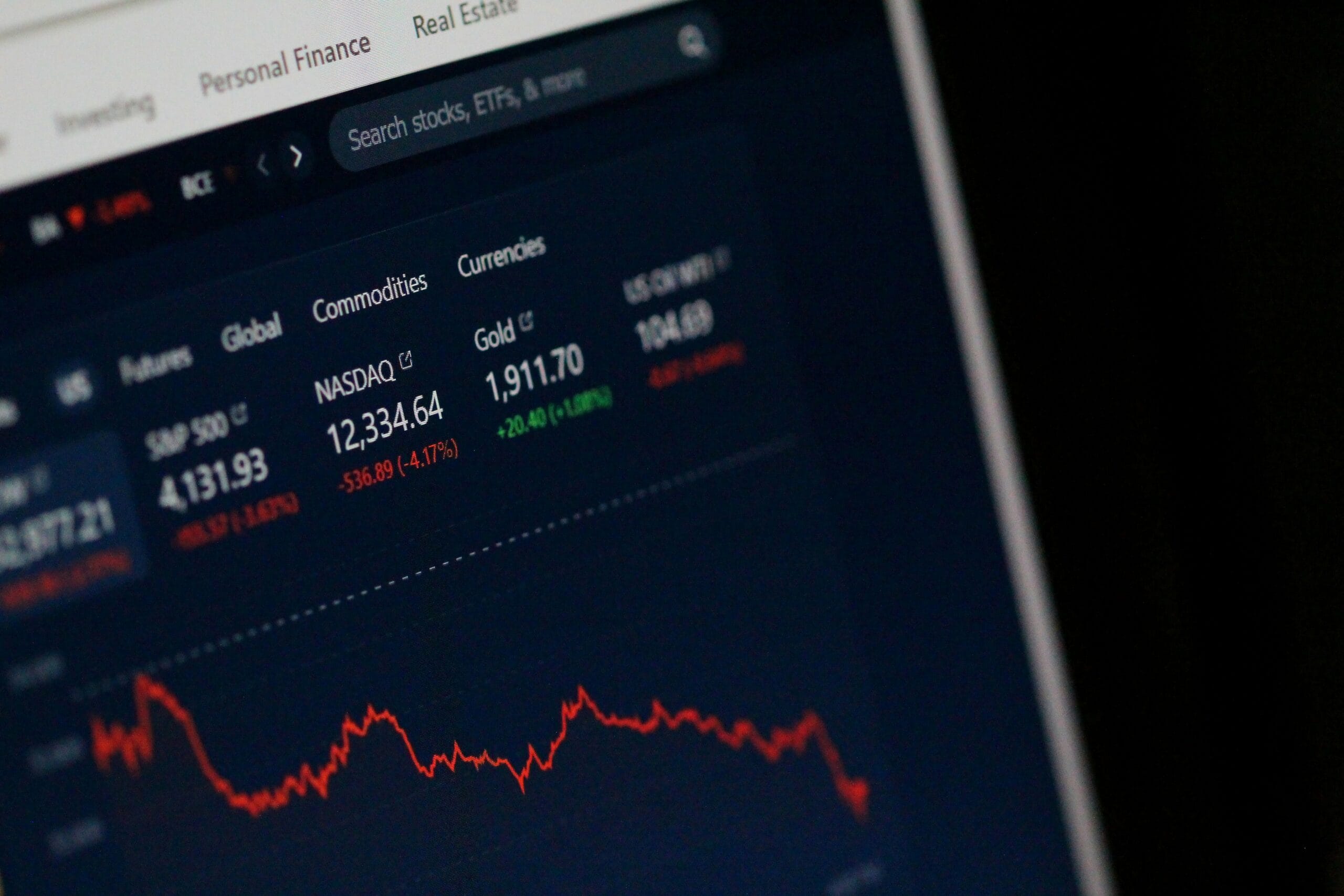
Introduction to Trade War Strategies
Trade wars represent a significant aspect of geopolitical dynamics and economic policies, manifesting as heightened tensions between nations due to economic disagreements. At their core, trade wars often arise from differing views on tariffs, trade balances, and market access, leading to reciprocal measures that can impact global trade flows. The implications of these conflicts can be substantial, affecting not only bilateral relations but also the international economy at large. Understanding trade wars is essential to navigating the complexities of modern economic interactions, particularly in the context of the United States and its primary trading partners.
During the Trump administration, a notable emphasis was placed on reshaping trade relationships, particularly with China. The imposition of tariffs on a variety of goods was central to Trump’s strategy, aimed at reducing the trade deficit and encouraging domestic manufacturing. These measures were framed as necessary steps to counteract what the administration characterized as unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and an unbalanced trading environment favoring China. The strategies employed were marked by a confrontational approach, which not only redefined the economic landscape but also polarized opinions on the effectiveness of such tactics in fostering long-term benefits for the American economy.
As we progress into new political landscapes, the vision of leaders like J.D. Vance is increasingly relevant. Vance, a prominent political figure, acknowledges the challenges posed by global trade and seeks to advocate for strategies that prioritize American workers while maintaining competitive markets. His perspective on trade war strategies will likely address the need for sustaining economic growth without alienating critical international partnerships. This evolving narrative encourages a re-evaluation of past strategies and serves as a foundation for future policies aimed at balancing national interests with global trade realities.
The Landscape of U.S.-China Trade Relations
Trade relations between the United States and China have a complex and multifaceted history that has evolved over several decades. The relationship began to formalize in the late 1970s, following China’s shift towards a more market-oriented economy under the leadership of Deng Xiaoping. The normalization of diplomatic ties in 1979 opened the door for increased trade and investment flows between these two economic giants. However, it was not without challenges and controversies.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, several trade agreements were established aimed at reducing tariffs and enhancing trade cooperation. The United States granted China Most Favored Nation status, which allowed for favorable trading terms. However, issues such as intellectual property theft, currency manipulation, and unfair trade practices began to emerge as significant points of contention. The perception of China as a potential economic threat grew particularly in the early 2000s, coinciding with China’s entry into the World Trade Organization in 2001.
The early 2000s marked a significant increase in U.S.-China trade, leading to significant trade imbalances. As American companies outsourced manufacturing jobs to China, concerns arose regarding job losses in the United States—especially within the manufacturing sector. The erosion of these jobs became a rallying point for political discourse, particularly during the 2016 presidential campaign, where trade policies took center stage.
Under President Trump, the trade relationship reached a breaking point, resulting in the initiation of a trade war characterized by tariffs and retaliatory measures. The implications of these strategies were profound, impacting manufacturing jobs, supply chains, and the global economy. As we examine the current landscape, it is crucial to consider the historical context of these trade relations, as past policies and disputes have undoubtedly shaped the present dynamics between the United States and China.
Trump’s Approach to China Policy
During his presidency, Donald Trump’s administration adopted a confrontational approach to China, marked by the implementation of tariffs and aggressive trade negotiations. One of the cornerstone strategies was the imposition of tariffs on a range of Chinese goods, which was intended to address what the Trump administration characterized as unfair trade practices and to reduce the substantial trade deficit between the United States and China. These tariffs, often referred to as “Section 301 tariffs,” affected billions of dollars worth of imports and were aimed at pressuring China to change its policies regarding intellectual property theft and forced technology transfers.
The trade negotiations under Trump’s administration were marked by a series of high-stakes meetings and talks with Chinese officials. The objective was not only to secure better trade terms but also to fundamentally alter the dynamics of the U.S.-China trade relationship. In phase one of the trade deal, signed in January 2020, China agreed to purchase more American goods, including agricultural products, in an effort to balance the trade scales. However, the long-term impact of these agreements remains a topic of debate among economists and policymakers.
Furthermore, Trump’s policies significantly impacted American industries, especially in manufacturing. The tariffs aimed at curbing imports led to higher costs for domestic manufacturers reliant on Chinese components, ultimately influencing pricing and consumer options in the U.S. market. While certain sectors, such as steel and aluminum, benefitted from protective tariffs, others faced challenges due to increased costs and reduced access to international supply chains. Overall, Trump’s China policy generated a substantial shift in American economic strategy, laying the groundwork for ongoing tensions that would shape U.S.-China relations in the years to come.
The Role of Tariffs in Trump’s Trade War
During his presidency, Donald Trump employed tariffs as a crucial instrument in his trade war strategy, aiming primarily to protect American industries and reduce the trade deficit with countries like China. The rationale behind imposing these tariffs was grounded in a belief that levying additional taxes on imported goods would encourage consumers to favor domestically produced items, thereby boosting local economies. Trump asserted that these tariffs were essential for safeguarding U.S. jobs and revitalizing sectors adversely affected by foreign competition.
A wide array of goods was targeted by these tariffs, including steel and aluminum, electronics, machinery, and agricultural products. For instance, the tariffs on steel and aluminum sought to shield American manufacturers from what was perceived as unfair pricing. However, this strategy did not come without consequences. Consumers faced higher prices as the cost of imported goods rose due to the added tariffs. This prompted concerns among various sectors, especially manufacturing and retail, which ultimately led to increased production costs and, in some cases, diminished profit margins.
The economic implications extended beyond immediate price increases; they fostered uncertainty in the market. Many businesses found themselves adjusting supply chains, contemplating the long-term effects of tariffs on their operations. This environment of unpredictability challenged established trade relations and sometimes led to retaliatory tariffs from affected countries. International responses included measures taken by China to levy tariffs on American products, notably agricultural exports, highlighting the interconnectedness of global markets.
Domestically, while some voters supported the president’s tough stance against unfair trade practices, others criticized the effectiveness of this strategy. The polarized reception suggested a deeper divide in opinions about trade policies and the far-reaching effects tariffs could have on the U.S. economy. As the implications of Trump’s tariff policies continue to unfold, they remain a salient point of discussion in the context of future trade strategies.
Impact on Manufacturing Jobs
The trade policies implemented during the Trump administration have significantly altered the landscape of manufacturing jobs in America. Notably, these strategies aimed to revitalize the domestic industry by imposing tariffs on imported goods, encouraging a shift towards local production. However, the consequences of such measures have been mixed, particularly in terms of employment levels within the manufacturing sector.
In the immediate aftermath of the tariffs, many manufacturers reported a surge in domestic production, leading to a temporary increase in manufacturing jobs. Proponents of these policies argued that by prioritizing American-made products, the U.S. economy would witness not only job growth but also a reduction in the trade deficit. Yet, this perspective did not universally resonate across the industry. Numerous manufacturing firms, especially those reliant on global supply chains, faced heightened operational costs leading to layoffs rather than new hiring. Factory workers expressed anxiety over job security, as rising material costs resulted from the tariffs, which in some instances meant reduced competitiveness for American products overseas.
Industry leaders have echoed these sentiments, highlighting the complexities intertwined with Trump’s trade policies. While there are sectors that experienced growth, such as steel and aluminum production, others have struggled to maintain workforce stability. The dilemma faced by many companies involved balancing the need for localized production with the economic realities of sourcing costs and market demands. Consequently, the fluctuation in manufacturing employment levels reflects broader trends in the job market, with many workers uttering concerns over the sustainability of jobs created in this environment of economic uncertainty.
Ultimately, the impact of these trade policies on manufacturing jobs serves as a microcosm of the pervasive effects of the trade war, necessitating a nuanced examination of future strategies aimed at fostering sustainable employment in the sector.
Vance’s Vision for Future Trade Policies
J.D. Vance, an influential political figure and author, has emerged as a candidate who aims to reshape America’s trade policy in the wake of the Trump administration. His vision encompasses a pragmatic approach to trade, particularly focusing on reducing the adverse economic impacts of trade with China. Vance’s stance underscores a commitment to revitalizing the manufacturing sector, which has faced significant challenges due to globalization and competition from overseas markets.
At the core of Vance’s strategy is the belief that a robust manufacturing base is essential for the long-term stability of the U.S. economy. He advocates for policies that incentivize domestic production and support industries that have been undermined by foreign competition. By promoting the idea of “reshoring” jobs, Vance envisions a future where American workers benefit from increased employment opportunities in homegrown industries. This strategy not only aims to generate jobs but also seeks to restore the pride and vitality of American communities that have been economically devastated in recent decades.
Another critical aspect of Vance’s policy framework involves tariffs and protectionism. While he recognizes that these tools can be valuable in curtailing unfair trade practices and leveling the playing field, he approaches their implementation with caution. His perspective is that tariffs should be used strategically and in conjunction with broader reforms that facilitate international trade relations without compromising domestic interests. Vance emphasizes the need for a comprehensive economic strategy that integrates trade policy with other elements of national growth, such as workforce development and technological innovation.
In conclusion, J.D. Vance’s vision for future trade policies is marked by a commitment to revitalizing American manufacturing, cautious yet strategic use of tariffs, and an overarching aim to foster sustainable economic growth. His approach reflects an understanding of the complexities inherent in international trade, positioning him as a thoughtful advocate for a new chapter in U.S. economic policy.
Public Opinion and Political Implications
The trade war initiated during Donald Trump’s presidency has substantially influenced public opinion and the political landscape in the United States. Polling data reveals a significant divide among different demographics regarding the effectiveness and consequences of Trump’s trade policies. The trade war, particularly with China, was framed as a protectionist stance aimed at revitalizing American manufacturing and safeguarding jobs. However, the prolonged tariffs led to increased prices for consumers and uncertainty among businesses, creating mixed reactions among voters.
A survey conducted by the Pew Research Center indicated that views on the trade war vary considerably between political affiliations. Republicans largely supported Trump’s tactics, seeing them as a necessary measure to address unfair trade practices. Conversely, many Democrats and independent voters expressed concerns about the economic repercussions, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on imports. This divergence highlights the complexity of public sentiment surrounding trade issues and how they can shape political narratives.
The recent rise of figures like J.D. Vance signals a shifting dialogue. Vance’s alignment with some of Trump’s views on trade, combined with a recognition of the challenges faced by working-class Americans, may resonate with voters looking for a blend of traditional conservatism and innovative solutions. As the political arena evolves, understanding the nuances of public opinion on trade will be crucial for candidates aiming to connect with constituents.
Furthermore, the economic implications of the trade war continue to impact voter sentiment. Regions affected by job losses or reduced wages are likely to scrutinize political candidates’ positions on trade more critically. As election cycles approach, candidates must navigate these complex dynamics, adapting their messages to address the concerns of their constituents while considering the broader implications on the political landscape.
Lessons Learned from the Trade War
The trade war initiated by former President Donald Trump against China brought several significant lessons to light regarding trade practices and policies. One of the most notable aspects was the importance of understanding economic interdependence. The tariffs imposed aimed to protect American industries, particularly in steel and aluminum, but they also led to retaliatory measures from China, which impacted U.S. farmers and manufacturers. This revealed a critical insight: unilateral trade measures often lead to unintended consequences that can ripple through various sectors of the economy.
Moreover, the trade war underscored the importance of strategic communication. Transparency in the goals of trade policies plays a vital role in ensuring that stakeholders, including businesses and consumers, understand the rationale behind such moves. Clear communication can mitigate confusion and anxiety in markets, ultimately aiding in maintaining economic stability. Additionally, the lack of coordination with allies during this trade conflict raised questions about the effectiveness of a confrontational approach. Cooperation with other nations could have strengthened the United States’ position against China by presenting a united front in negotiations.
The trade war also illuminated the necessity of adaptability. While some American businesses managed to pivot and thrive by seeking alternative markets, others struggled to cope with the rapid shift in the trade landscape. The ability to adjust supply chains and explore new partnerships is crucial for resilience in a globalized economy. As companies evaluate their operations, understanding the lessons from the past becomes essential for future strategic planning.
In conclusion, the U.S. trade war with China provided valuable insights into the complexities of international trade. Balancing protective measures with cooperation, maintaining clear communication, and fostering adaptability can significantly inform future policies in a manner that promotes economic growth both domestically and internationally.
Conclusion: Reflecting on the Future of U.S.-China Trade
The U.S.-China trade relationship has been influenced significantly by the strategic decisions of past and present leadership, particularly during the Trump administration and the proposed policies of figures like J.D. Vance. Trump’s tenure marked a turning point, as his administration prioritized aggressive trade measures, including tariffs aimed at curbing Chinese import practices. This approach sought to protect American jobs and industries, aligning with a more nationalist economic policy. However, these strategies came with their own set of complexities, leading to increased prices for consumers and tensions in international relations.
As we look to the future, Vance’s vision introduces a potential shift towards more cooperative measures that emphasize rebuilding manufacturing in the U.S., while still addressing concerns over trade imbalances and intellectual property theft. This dual approach seeks to balance a competitive stance with the necessity of engaging China as a critical partner in global trade. Vance advocates for policies that could promote innovation and strategic industries in America, while supporting fair practices that foster a sustainable economic environment between the two nations.
In light of these differing approaches, the future of U.S.-China trade remains uncertain. Potential outcomes depend on how new policies are articulated and implemented, taking into consideration global economic shifts and emerging challenges. The interactions between economic strategies will be crucial, not only for the bilateral relationship but also for the broader economic landscape. An understanding of Trump’s legacy combined with thoughtful adaptations proposed by leaders like Vance may pave the way for a more balanced and fruitful U.S.-China trade relationship. Ultimately, ongoing dialogue and strategic negotiation will be key to navigating this complex terrain effectively.
- Bond Market Has €400 Billion Check Ready for Germany to Spend
- Trump Team Background Checks, Markets Embrace Bessent, More
- Adani Trouble Risks Hurting India’s Hottest Sector Driving Growth
- Markets React to Treasury Pick, Trump Transition Follow Up, More
- Bessent Pick Reactions, Earnings This Week, More
- The week ahead in Asia
- Huawei to launch smartphone with own software in latest sign of China-US splintering
- UK business cutting back growth plans after Budget tax rises, warns CBI
- US retailers stretch out Black Friday deals to lure flagging shoppers
- ‘Wicked’ and ‘Gladiator II’ give Hollywood hope for strong holiday box office
- New Universal Theme Park Featuring Mario And Harry Potter Opens In May—Here’s What We Know
- 13 Best Flower Delivery Services To Show Your Love From Miles Away
- What We Know About The Nicki Minaj-Megan Thee Stallion Feud—From ‘Hiss’ To ‘Big Foot’
- Taylor Swift At The Super Bowl: The Conspiracy Theory, Explained
- Crypto Is Suddenly Braced For A Huge China Earthquake After Bitcoin, Ethereum, XRP And Solana Price Surge